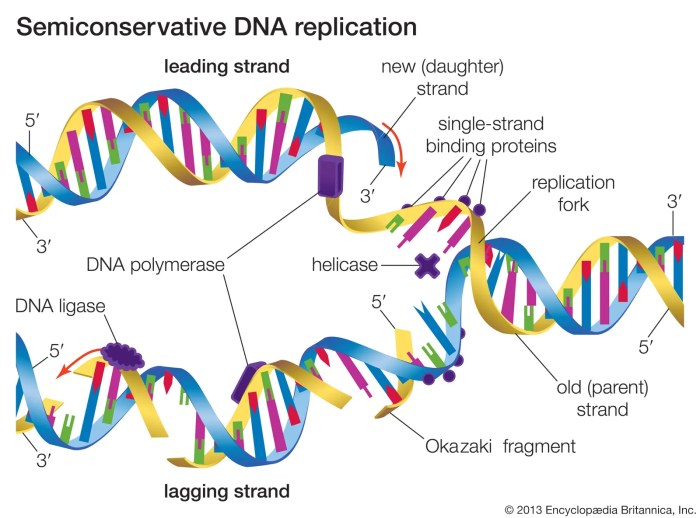
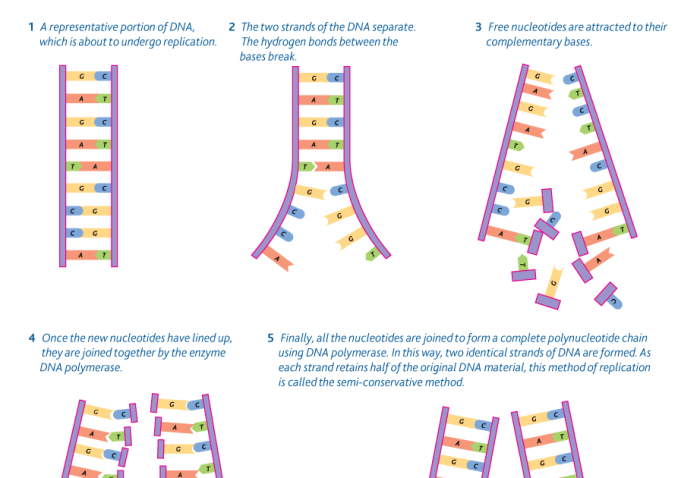
Model 3 timing of dna replication – Model 3 DNA replication timing, an intricate process that governs the precise duplication of genetic material in specific organisms, presents a fascinating area of study in molecular biology. This phenomenon holds profound implications for cellular function and organismal development.
Understanding the timing of DNA replication in Model 3 organisms is crucial for unraveling the mechanisms underlying genome stability, gene expression, and cellular differentiation. In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into the factors influencing replication timing, the experimental techniques employed to study it, and the consequences of its alteration.
Model 3 Timing of DNA Replication
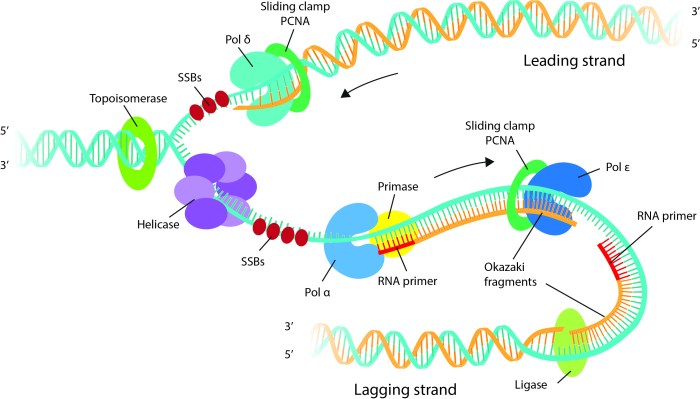
Model 3 organisms, such as Arabidopsis thaliana and Caenorhabditis elegans, have well-defined DNA replication timing programs that ensure the precise duplication of their genomes during each cell cycle. These programs are influenced by various factors, including chromatin structure, gene expression, and DNA damage.
The timing of DNA replication is crucial for proper cell function and development. Alterations in DNA replication timing can lead to genomic instability, developmental abnormalities, and increased susceptibility to disease.
Experimental Techniques for Studying DNA Replication Timing
Several experimental techniques are used to study DNA replication timing in Model 3 organisms. These techniques include:
- BrdU incorporation assays:This technique involves labeling replicating DNA with the thymidine analog BrdU, which can be detected using antibodies.
- DNA combing:This technique involves stretching DNA fibers and visualizing the replication forks using fluorescent probes.
- ChIP-seq:This technique involves immunoprecipitating proteins bound to DNA and sequencing the DNA fragments to identify replication origins.
Each technique has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of technique depends on the specific question being investigated.
Replication Timing Programs
Replication timing programs are the patterns of DNA replication across the genome. These programs are conserved across different cell types and developmental stages and are thought to be regulated by a combination of genetic and epigenetic factors.
There are two main types of replication timing programs:
- Early-replicating regions:These regions replicate early in S phase and are typically gene-rich and euchromatic.
- Late-replicating regions:These regions replicate late in S phase and are typically gene-poor and heterochromatic.
The existence of replication timing programs is supported by a variety of evidence, including:
- Genome-wide studies:These studies have shown that the timing of DNA replication is consistent across different cell types and developmental stages.
- Mutation analysis:Mutations in genes involved in DNA replication timing can lead to changes in the replication timing of specific regions of the genome.
- Epigenetic studies:Epigenetic modifications, such as DNA methylation and histone modifications, have been shown to influence DNA replication timing.
Replication Timing and Gene Expression, Model 3 timing of dna replication
There is a close relationship between replication timing and gene expression. Early-replicating regions are typically gene-rich and have higher levels of gene expression than late-replicating regions.
Several mechanisms have been proposed to explain the link between replication timing and gene expression. One possibility is that the accessibility of DNA to the transcriptional machinery is influenced by replication timing. Another possibility is that replication timing influences the epigenetic modifications of DNA, which in turn affects gene expression.
There are several examples of how replication timing can regulate gene expression in Model 3 organisms. For example, in Arabidopsis thaliana, the early-replicating gene FLC is required for the vernalization response, which is a process that allows plants to flower in response to cold temperatures.
Replication Timing and Genome Architecture
Replication timing is also closely linked to genome architecture. Early-replicating regions are typically located in euchromatic regions of the genome, while late-replicating regions are typically located in heterochromatic regions.
There is evidence to suggest that replication timing plays a role in shaping genome architecture. For example, in Arabidopsis thaliana, the early-replicating regions are enriched for genes involved in transcription and translation, while the late-replicating regions are enriched for genes involved in DNA repair and recombination.
Questions Often Asked: Model 3 Timing Of Dna Replication
What factors influence DNA replication timing in Model 3 organisms?
Factors such as chromatin structure, transcription activity, and DNA methylation patterns are known to influence the timing of DNA replication.
What are the consequences of altered DNA replication timing in Model 3 organisms?
Altered DNA replication timing can lead to genomic instability, developmental abnormalities, and increased susceptibility to diseases such as cancer.
What experimental techniques are used to study DNA replication timing in Model 3 organisms?
Techniques such as DNA combing, BrdU labeling, and ChIP-seq are commonly employed to study DNA replication timing.