Embark on an educational journey with our comprehensive Cell Membrane and Transport WebQuest Answer Key, meticulously crafted to illuminate the intricacies of cellular transport mechanisms. This invaluable resource delves into the structure, functions, and dynamics of the cell membrane, providing a profound understanding of its role in maintaining cellular homeostasis and facilitating essential life processes.
As we explore the diverse mechanisms of membrane transport, including passive and active transport, you will gain insights into how substances traverse the cell membrane, defying concentration gradients and driving cellular processes. Our exploration extends to the impact of membrane transport on plant cell growth and development, unraveling the unique adaptations that enable plants to thrive in diverse environments.
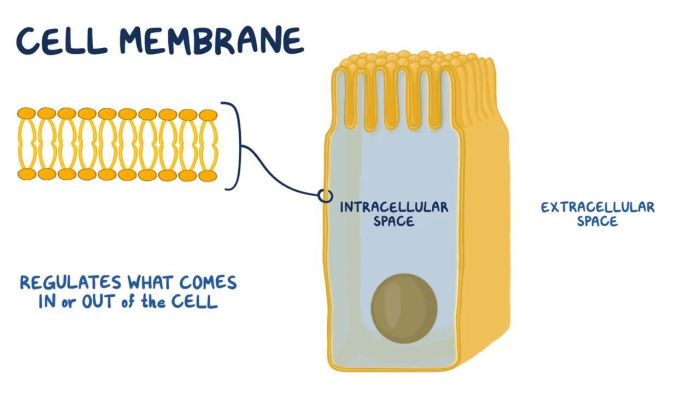
Cell Membrane Overview

The cell membrane is a thin, flexible barrier that surrounds all cells. It is composed of a phospholipid bilayer, which is a double layer of phospholipids. Phospholipids are molecules that have a hydrophilic (water-loving) head and a hydrophobic (water-hating) tail.
The hydrophilic heads face outward, towards the aqueous environment, while the hydrophobic tails face inward, away from the water. This arrangement creates a barrier that is impermeable to most molecules.
The cell membrane also contains proteins. These proteins can be embedded in the lipid bilayer, or they can be attached to the surface of the membrane. Membrane proteins play a variety of roles, including:
- Transporting molecules across the membrane
- Recognizing and binding to other cells
- Transducing signals from the outside of the cell to the inside
Functions of the Cell Membrane
The cell membrane has a number of important functions, including:
- Protection:The cell membrane protects the cell from its surroundings. It prevents harmful substances from entering the cell and it keeps the cell’s contents from leaking out.
- Transport:The cell membrane controls the movement of molecules into and out of the cell. It allows nutrients to enter the cell and it removes waste products from the cell.
- Communication:The cell membrane contains receptors that allow the cell to communicate with other cells. These receptors bind to specific molecules, which triggers a response inside the cell.
- Cell recognition:The cell membrane contains glycoproteins that allow the cell to recognize other cells. These glycoproteins bind to specific molecules on the surface of other cells, which helps the cells to identify each other.
Visual Representation of the Cell Membrane, Cell membrane and transport webquest answer key
| Component | Structure | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Phospholipids | A double layer of phospholipids with hydrophilic heads and hydrophobic tails | Forms a barrier that is impermeable to most molecules |
| Proteins | Embedded in the lipid bilayer or attached to the surface of the membrane | Transport molecules, recognize and bind to other cells, transduce signals |
| Carbohydrates | Attached to proteins or lipids on the surface of the membrane | Cell recognition, cell-cell communication |
FAQ Explained: Cell Membrane And Transport Webquest Answer Key
What is the primary function of the cell membrane?
The cell membrane acts as a selectively permeable barrier, regulating the entry and exit of substances into and out of the cell.
Explain the difference between passive and active transport.
Passive transport involves the movement of substances down a concentration gradient, requiring no energy input, while active transport utilizes energy to move substances against a concentration gradient.
How does membrane permeability influence transport rates?
Membrane permeability determines the ease with which substances can cross the membrane, affecting the rate of transport.