Parallel lines cut by a transversal digital escape – Parallel lines cut by a transversal is a captivating subject that unveils the intricate relationships between lines and angles. As we delve into this realm, we’ll unravel the properties, applications, and geometric constructions that stem from this fundamental concept, illuminating its significance in the world of mathematics.
The concept of parallel lines and transversals forms the cornerstone of this exploration, laying the foundation for understanding the angle relationships that arise when these lines intersect. We’ll delve into the properties of corresponding angles, alternate interior angles, and alternate exterior angles, revealing their interconnectedness and the patterns they form.
Introduction to Parallel Lines Cut by a Transversal: Parallel Lines Cut By A Transversal Digital Escape
Parallel lines are two lines that never intersect. A transversal is a line that intersects two or more other lines. When a transversal intersects two parallel lines, it creates eight angles.
The following illustration shows two parallel lines, l and m, cut by a transversal, t:

Properties of Parallel Lines Cut by a Transversal, Parallel lines cut by a transversal digital escape
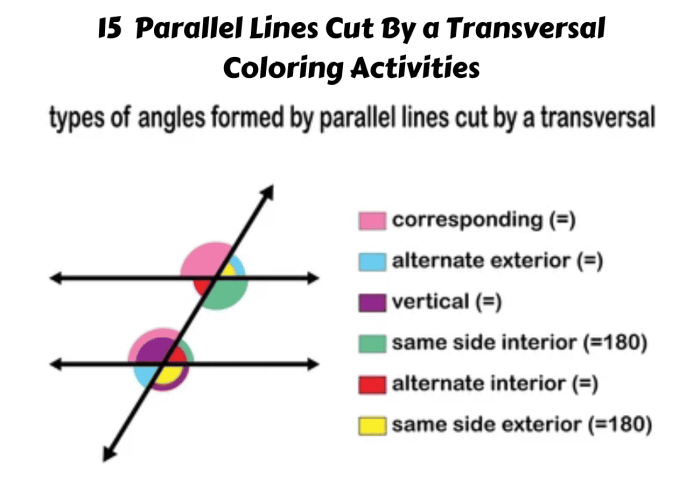
When a transversal intersects two parallel lines, it creates eight angles. These angles are related to each other in specific ways:
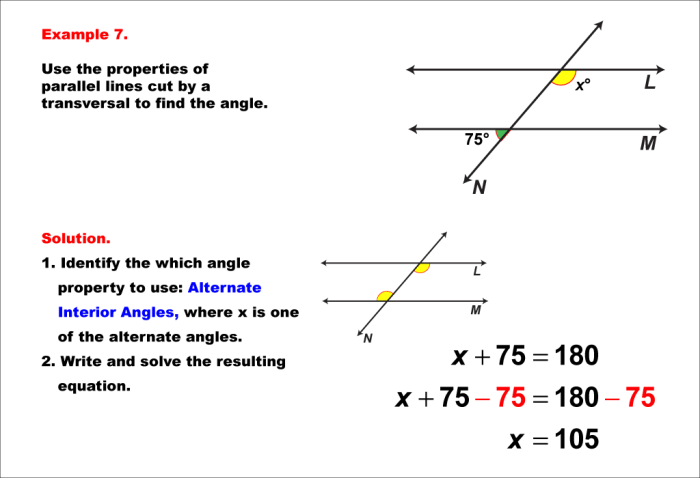
- Corresponding anglesare angles that are in the same position on opposite sides of the transversal. Corresponding angles are congruent.
- Alternate interior anglesare angles that are on the inside of the parallel lines and on opposite sides of the transversal. Alternate interior angles are congruent.
- Alternate exterior anglesare angles that are on the outside of the parallel lines and on opposite sides of the transversal. Alternate exterior angles are congruent.
Applications of Parallel Lines Cut by a Transversal
Parallel lines and transversals are used in a variety of real-world applications, including:
- Architecture:Parallel lines are used to create the walls, floors, and ceilings of buildings. Transversals are used to create doors, windows, and other openings.
- Surveying:Parallel lines and transversals are used to measure distances and angles. This information is used to create maps and to design roads and other structures.
- Navigation:Parallel lines and transversals are used to navigate ships and airplanes. The angles between the lines and the transversal can be used to determine the direction and distance to a destination.
Geometric Constructions
Parallel lines and transversals can be used to construct a variety of geometric shapes, including:
- Rectangles:Rectangles are quadrilaterals with four right angles. To construct a rectangle, draw two parallel lines and then draw two transversals that intersect the parallel lines at right angles.
- Parallelograms:Parallelograms are quadrilaterals with two pairs of parallel sides. To construct a parallelogram, draw two parallel lines and then draw two transversals that intersect the parallel lines at any angle.
- Trapezoids:Trapezoids are quadrilaterals with one pair of parallel sides. To construct a trapezoid, draw two parallel lines and then draw two transversals that intersect the parallel lines at any angle.
Advanced Topics
Parallel lines and transversals are also used in more advanced geometry topics, such as:
- The Pythagorean Theorem:The Pythagorean Theorem states that in a right triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the other two sides.
- The Law of Sines:The Law of Sines is a trigonometric formula that relates the lengths of the sides of a triangle to the sines of the angles opposite those sides.
These concepts are used in a variety of geometric proofs and applications.
Essential FAQs
What is the definition of parallel lines?
Parallel lines are two lines that never intersect, no matter how far they are extended.
What is a transversal?
A transversal is a line that intersects two or more other lines.
What are the different types of angle relationships created when parallel lines are cut by a transversal?
Corresponding angles are angles that are in the same position on opposite sides of the transversal. Alternate interior angles are angles that are on opposite sides of the transversal and inside the parallel lines. Alternate exterior angles are angles that are on opposite sides of the transversal and outside the parallel lines.