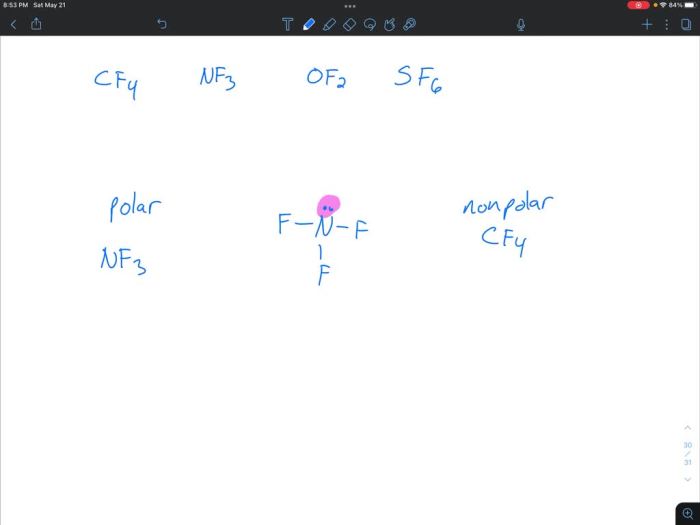
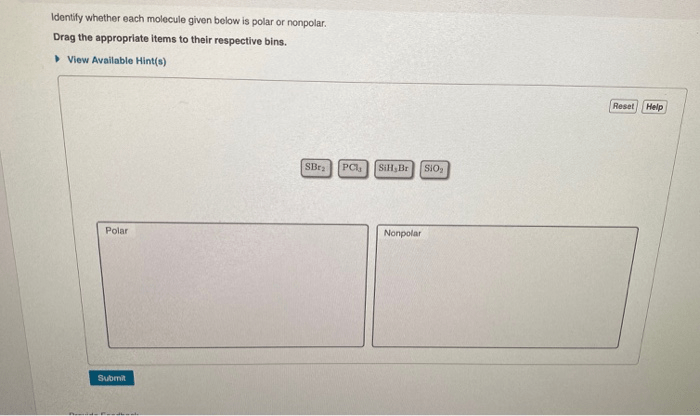
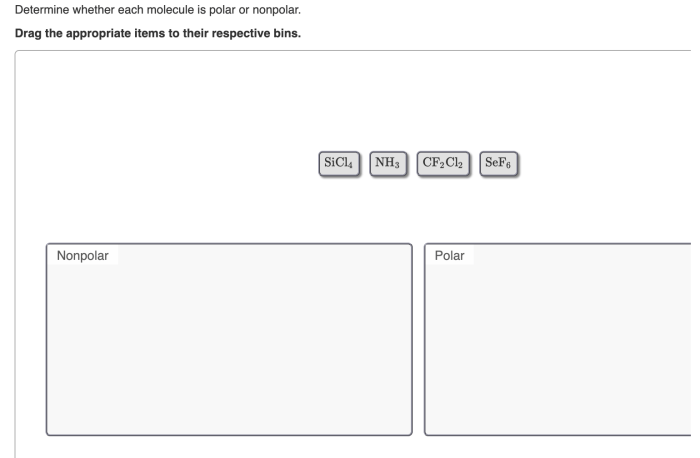
Determine whether each molecule given below is polar or nonpolar. – Determining whether a molecule is polar or nonpolar is crucial in understanding its physical and chemical properties. This analysis involves examining molecular structure, electronegativity differences, and bond polarities, providing insights into molecular behavior and reactivity.
By understanding these concepts, scientists can predict various properties such as solubility, boiling point, and reactivity, enabling advancements in fields such as drug design, materials science, and environmental chemistry.
Polarity of Molecules: Determine Whether Each Molecule Given Below Is Polar Or Nonpolar.
The polarity of a molecule refers to its separation of electric charge, resulting in a net positive or negative charge. Understanding molecular polarity is crucial in predicting the physical and chemical properties of substances.
Identify Molecular Structure
Molecular structure plays a vital role in determining polarity. Molecules can adopt various shapes, including linear, bent, trigonal planar, and tetrahedral. The arrangement of atoms and the presence of lone pairs affect the distribution of electrons and, consequently, the polarity of the molecule.
Determine Electronegativity Differences, Determine whether each molecule given below is polar or nonpolar.
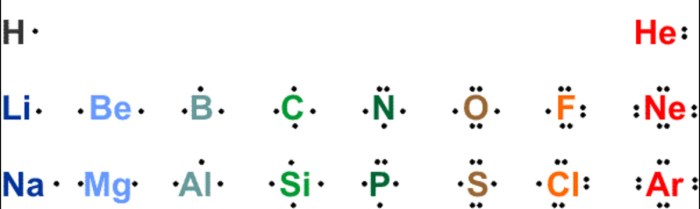
Electronegativity measures an atom’s ability to attract electrons. Different atoms within a molecule may have varying electronegativities, leading to unequal sharing of electrons. The greater the electronegativity difference between atoms, the more polar the bond formed between them.
| Element | Electronegativity |
|---|---|
| Fluorine (F) | 4.0 |
| Oxygen (O) | 3.5 |
| Nitrogen (N) | 3.0 |
| Carbon (C) | 2.5 |
| Hydrogen (H) | 2.1 |
Analyze Bond Polarity
Bond polarity arises when electrons are unequally distributed within a covalent bond. This occurs due to differences in electronegativity between the bonded atoms. The more electronegative atom attracts electrons more strongly, creating a partial negative charge on itself and a partial positive charge on the less electronegative atom.
Evaluate Molecular Polarity
Molecular polarity is determined by the combined effect of molecular structure, electronegativity differences, and bond polarities. A molecule is considered polar if it has a net positive or negative charge due to the unequal distribution of electrons. Nonpolar molecules, on the other hand, have no net charge and their electrons are evenly distributed.
FAQ Insights
What is the significance of molecular polarity?
Molecular polarity influences intermolecular interactions, solubility, and reactivity, affecting the physical and chemical properties of substances.
How does electronegativity contribute to molecular polarity?
Electronegativity differences between atoms within a molecule create an uneven distribution of electrons, resulting in bond polarity and, potentially, molecular polarity.
What is the relationship between bond polarity and molecular polarity?
Bond polarities contribute to molecular polarity. The cumulative effect of polar bonds within a molecule determines its overall polarity.