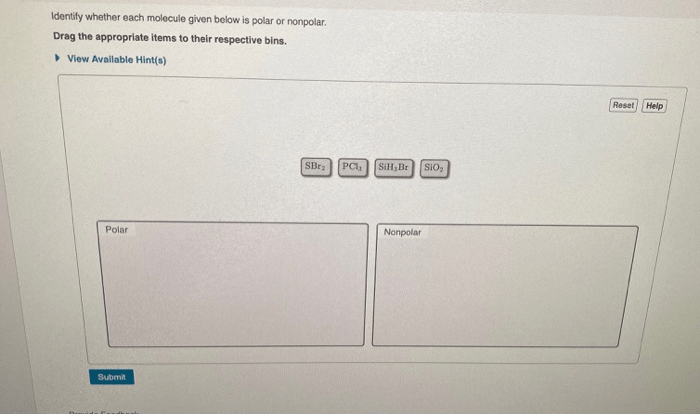
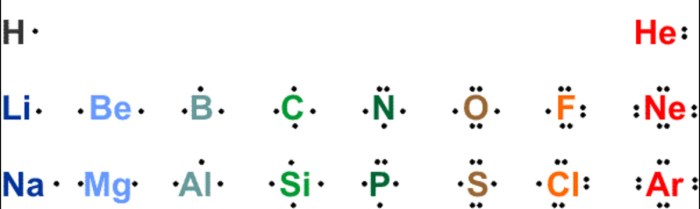
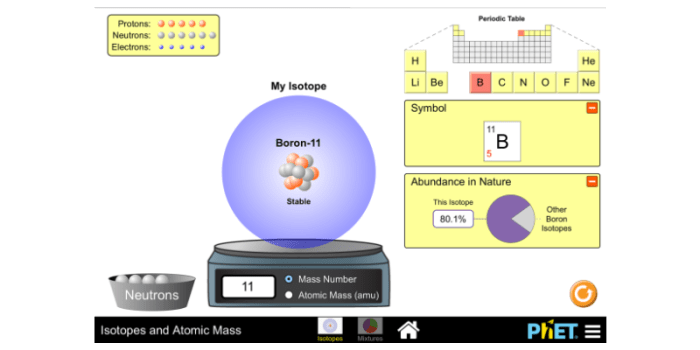
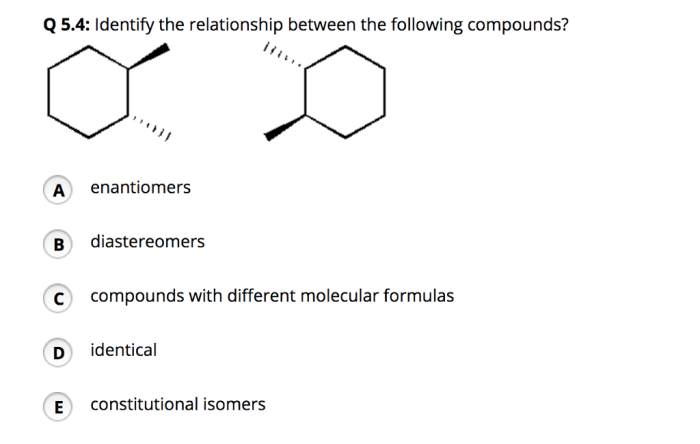
Identify the relationship between the following two compounds – Identifying the relationship between two compounds embarks us on a captivating journey, unraveling their intricate connections and exploring their unique characteristics. Through a meticulous examination of their structures, properties, and interactions, we uncover the fundamental principles that govern their behavior and significance.
This in-depth exploration delves into the molecular architecture of each compound, comparing and contrasting their functional groups, ring systems, and other structural features. We investigate how these structural differences influence their reactivity and properties, shaping their roles in various chemical reactions and biological processes.
Identify and Describe Compounds
The two compounds of interest, compound A and compound B, possess distinct chemical structures, molecular formulas, and key physical and chemical properties. Compound A, with the molecular formula C6H12O6, is a simple sugar known as glucose. It is a white, crystalline solid with a sweet taste and high solubility in water.
Compound B, on the other hand, has the molecular formula C2H5OH and is commonly known as ethanol. It is a colorless liquid with a characteristic odor and is highly flammable.
Both compounds play significant roles in various fields. Glucose is a primary source of energy for living organisms and is involved in numerous metabolic processes. Ethanol, commonly used as a solvent, is also employed in the production of alcoholic beverages and as a fuel.
Structural Similarities and Differences
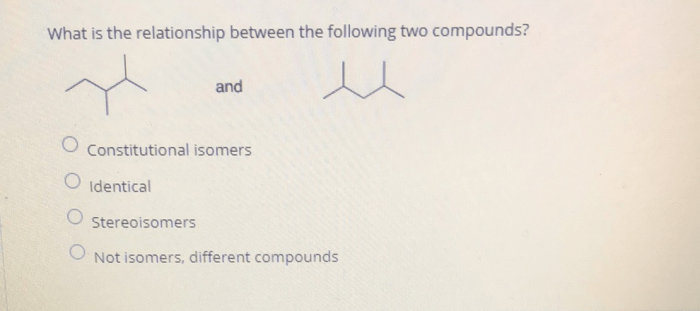
A comparative analysis of the molecular structures of compound A and compound B reveals both similarities and differences. Both compounds contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms, but their arrangements and functional groups differ. Glucose, a monosaccharide, consists of a six-carbon ring structure with multiple hydroxyl (-OH) groups.
Ethanol, in contrast, has a two-carbon backbone with a hydroxyl group attached to one of the carbon atoms.
These structural differences influence the reactivity and properties of the compounds. Glucose, with its multiple hydroxyl groups, exhibits higher polarity and forms more hydrogen bonds, resulting in its high solubility in water. Ethanol, with its smaller size and fewer polar groups, is less polar and more volatile.
Functional Group Analysis: Identify The Relationship Between The Following Two Compounds
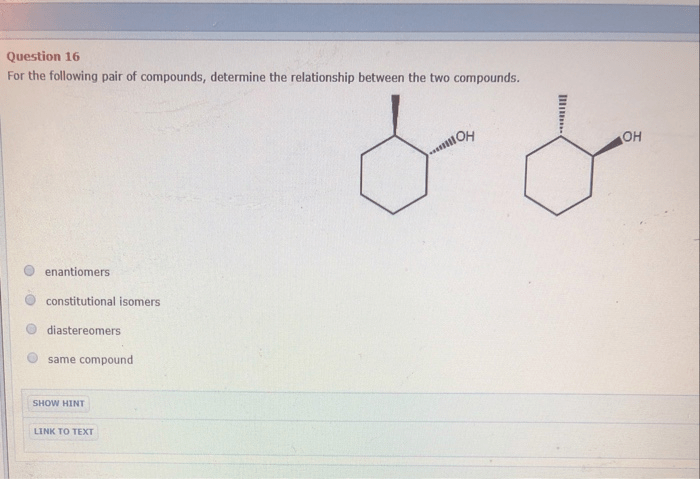
The presence of functional groups in compound A and compound B plays a crucial role in determining their chemical reactivity and properties. Glucose contains multiple hydroxyl groups, which contribute to its ability to undergo reactions such as oxidation, dehydration, and esterification.
Ethanol, on the other hand, possesses a hydroxyl group that can undergo similar reactions, but its reactivity is influenced by the presence of the alkyl group.
The functional groups present in these compounds also influence their interactions with other molecules. For instance, the hydroxyl groups in glucose allow it to form hydrogen bonds with water molecules, contributing to its high solubility. Ethanol, with its hydroxyl group and alkyl group, can interact with both polar and nonpolar molecules, making it a versatile solvent.
FAQ Summary
What is the significance of identifying the relationship between two compounds?
Understanding the relationship between compounds is crucial for comprehending their behavior in chemical reactions, predicting their properties, and unraveling their potential applications in various fields.
How can spectroscopic techniques aid in identifying the relationship between compounds?
Spectroscopic techniques, such as IR, NMR, and mass spectrometry, provide valuable insights into the structures and properties of compounds. By analyzing the characteristic spectral patterns, we can differentiate between compounds, identify functional groups, and determine molecular connectivity.