Aircraft maintenance logbook entry example – Aircraft maintenance logbook entries serve as vital documentation in the aviation industry, providing a detailed record of all maintenance activities performed on an aircraft. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of aircraft maintenance logbook entries, exploring their significance, components, types, best practices, legal requirements, and integration with maintenance management systems.
By understanding the nuances of aircraft maintenance logbook entries, maintenance personnel can ensure accurate and thorough documentation, contributing to the safety and reliability of aircraft operations.
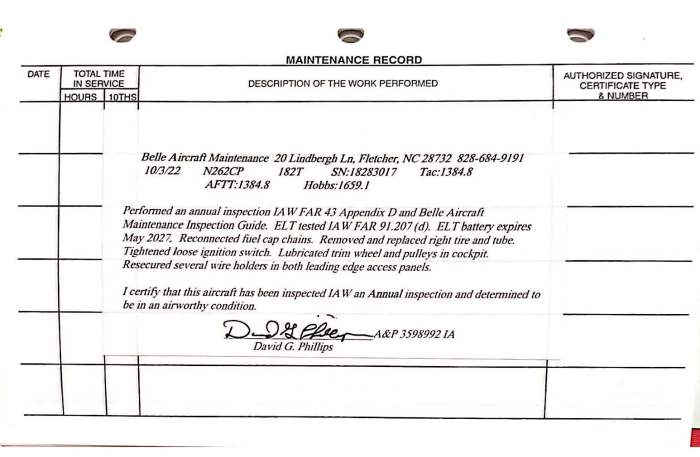
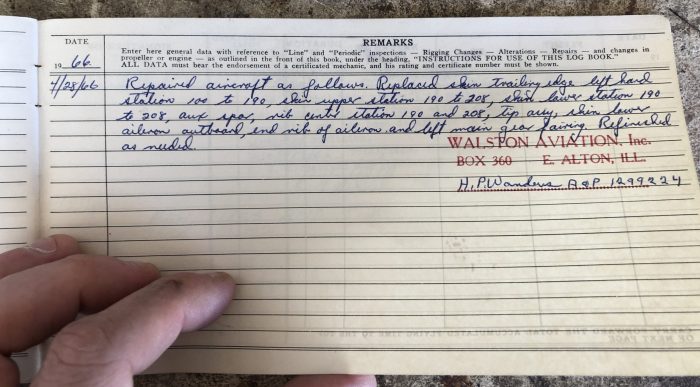
Aircraft Maintenance Logbook Entry Example

Aircraft maintenance logbook entries are essential for recording and tracking all maintenance performed on an aircraft. They provide a detailed record of the work that has been done, the parts that have been replaced, and the inspections that have been carried out.
This information is vital for ensuring the safety and airworthiness of the aircraft.
Logbook entries must be accurate, complete, and timely. They should be written in a clear and concise manner, using industry-standard abbreviations and terminology. The person making the entry should sign and date it, and the entry should be reviewed and approved by a qualified supervisor.
Components of a Logbook Entry, Aircraft maintenance logbook entry example
The essential elements of an aircraft maintenance logbook entry include:
- The date the work was performed
- The aircraft registration number
- The aircraft tail number
- The type of work performed
- The parts that were replaced
- The inspections that were carried out
- The person who performed the work
- The person who reviewed and approved the work
Types of Logbook Entries
There are different types of aircraft maintenance logbook entries, including:
- Routine maintenance entries
- Non-routine maintenance entries
- Inspection entries
- Repair entries
- Modification entries
Best Practices for Logbook Entries
Best practices for creating and maintaining aircraft maintenance logbook entries include:
- Use clear and concise language.
- Use industry-standard abbreviations and terminology.
- Be accurate and complete.
- Be timely.
- Sign and date the entry.
- Have the entry reviewed and approved by a qualified supervisor.
Legal and Regulatory Requirements
Aircraft maintenance logbook entries are required by law in most countries. The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) requires that all aircraft registered in the United States have a maintenance logbook. The logbook must be kept in the aircraft at all times and must be made available to the FAA upon request.
Non-compliance with the FAA’s regulations can result in fines and other penalties.
Use of Logbook Entries for Troubleshooting
Aircraft maintenance logbook entries can be used for troubleshooting by identifying potential issues and trends. By analyzing the entries, mechanics can identify recurring problems and take steps to prevent them from happening again.
For example, if a mechanic notices that a particular part has been replaced multiple times, they may investigate to determine the root cause of the problem and develop a solution to prevent it from happening again.
Integration with Maintenance Management Systems
Aircraft maintenance logbook entries can be integrated with maintenance management systems (MMS). MMSs are software programs that help airlines and other aircraft operators manage their maintenance operations. MMSs can track aircraft maintenance history, schedule maintenance tasks, and generate reports.
Integrating logbook entries with MMSs can improve efficiency and safety by providing a centralized repository for all maintenance information.
Data Analysis and Reporting
Aircraft maintenance logbook entries can be used for data analysis and reporting. By extracting and analyzing data from logbook entries, airlines and other aircraft operators can identify trends and patterns in maintenance events.
This information can be used to improve maintenance practices and reduce costs.
Training and Resources
There are a number of resources available to help aircraft mechanics and other personnel learn about aircraft maintenance logbook entries. These resources include:
- The FAA’s website
- The Aircraft Maintenance Technician Society (AMTS)
- The National Business Aviation Association (NBAA)
FAQ: Aircraft Maintenance Logbook Entry Example
What is the purpose of an aircraft maintenance logbook entry?
An aircraft maintenance logbook entry documents all maintenance activities performed on an aircraft, providing a detailed record for tracking maintenance history, troubleshooting issues, and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements.
What are the key components of a logbook entry?
Essential components of a logbook entry include the date, aircraft identification, type of maintenance performed, parts replaced or repaired, labor hours, and the signature of the authorized mechanic.
What are the different types of logbook entries?
Logbook entries can be classified into various types, such as routine maintenance entries, defect rectification entries, modification entries, and inspection entries.
What are the best practices for creating logbook entries?
Best practices for logbook entries involve using clear and concise language, providing detailed descriptions of maintenance activities, and adhering to industry standards and abbreviations.
What are the legal and regulatory requirements for logbook entries?
Logbook entries must comply with aviation regulations and industry standards, which may vary depending on the jurisdiction. Failure to maintain accurate and complete logbook entries can result in penalties and compromise aircraft safety.