Which of the following represent the Lewis structure for Cl? Understanding the Lewis structure of chlorine is crucial for comprehending its chemical properties and behavior. This article delves into the concept of Lewis structures, exploring the octet rule, resonance, molecular geometry, hybridization, and bond properties of chlorine.
The Lewis structure provides a visual representation of the arrangement of electrons in a molecule, offering insights into its chemical bonding and reactivity. By examining the Lewis structure of chlorine, we gain a deeper understanding of its molecular structure, stability, and interactions with other atoms and molecules.
Lewis Structure of Chlorine: Which Of The Following Represent The Lewis Structure For Cl
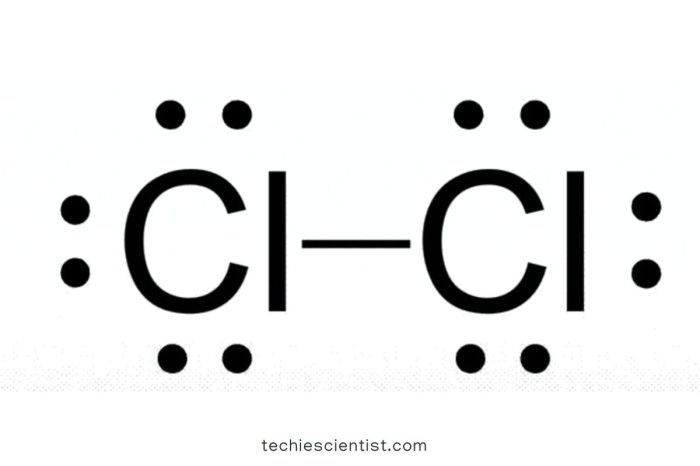
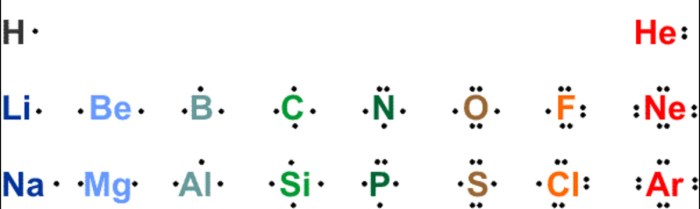
A Lewis structure is a diagram that represents the bonding between atoms in a molecule. It shows the arrangement of electrons in the valence shell of each atom, which are the outermost electrons that participate in chemical bonding. The Lewis structure of chlorine (Cl) is important because it helps us understand the chemical properties of this element.
The octet rule states that atoms are most stable when they have eight valence electrons. Chlorine has seven valence electrons, so it needs to gain one more electron to achieve a stable configuration. In the Lewis structure of chlorine, the two chlorine atoms share two electrons to form a covalent bond, resulting in each chlorine atom having eight valence electrons.
Drawing the Lewis Structure of Chlorine
To draw the Lewis structure of chlorine, follow these steps:
- Draw two chlorine atoms side by side.
- Place two dots between the chlorine atoms to represent the shared electrons.
- Add six dots around each chlorine atom to represent the remaining six valence electrons.
The resulting Lewis structure is:
Resonance Structures of Chlorine
The Lewis structure of chlorine can also be represented by two resonance structures. Resonance structures are different representations of the same molecule that have the same number of electrons and the same overall charge. In the case of chlorine, the two resonance structures are:
These two resonance structures are equivalent, and the actual structure of chlorine is a hybrid of the two.
Molecular Geometry of Chlorine
The molecular geometry of chlorine is determined by the VSEPR (valence shell electron pair repulsion) theory. VSEPR theory states that the geometry of a molecule is determined by the number of valence electron pairs around the central atom. In the case of chlorine, there are two valence electron pairs around the central chlorine atom, so the molecular geometry is linear.
Hybridization of Chlorine, Which of the following represent the lewis structure for cl
The hybridization of the chlorine atom in its Lewis structure is sp3. Hybridization is the mixing of atomic orbitals to form new orbitals with different shapes and energies. In the case of chlorine, the sp3 hybridization results in four equivalent orbitals that are directed towards the corners of a tetrahedron.
Bond Properties of Chlorine
The type of bond formed between chlorine atoms in the Lewis structure is a covalent bond. A covalent bond is formed when two atoms share electrons. In the case of chlorine, the two chlorine atoms share two electrons to form a single covalent bond.
The bond length of the chlorine-chlorine bond is 198 pm. The bond strength of the chlorine-chlorine bond is 242 kJ/mol.
Applications of Chlorine Lewis Structure
The Lewis structure of chlorine is used to understand the chemical properties of this element. For example, the Lewis structure helps to explain why chlorine is a reactive element. Chlorine is a reactive element because it has seven valence electrons, which means that it is one electron short of a stable octet configuration.
This makes chlorine likely to react with other elements to gain the electron it needs to achieve a stable configuration.
The Lewis structure of chlorine is also used to explain why chlorine is a good oxidizing agent. An oxidizing agent is a substance that can accept electrons from another substance. Chlorine is a good oxidizing agent because it has a high electronegativity, which means that it has a strong attraction for electrons.
Clarifying Questions
What is the octet rule?
The octet rule states that atoms tend to gain or lose electrons until they have eight valence electrons, achieving a stable electron configuration.
How many valence electrons does chlorine have?
Chlorine has seven valence electrons.
What is resonance?
Resonance is a concept that describes the delocalization of electrons in a molecule, resulting in multiple Lewis structures that contribute to the overall structure.